In July 2018, Google launched Chrome 68, introducing some minor changes like Page Lifecycle API, Payment Handler API, and plenty more. It was during that time that Google took a step closer to securing the web.
In Chrome 68, sites without HTTPS were marked as not secure.
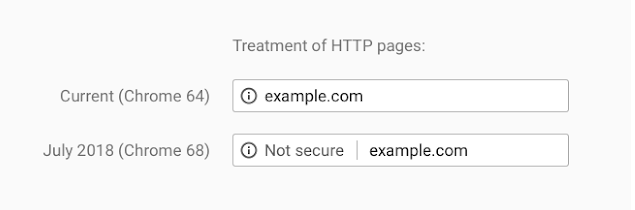
If users come across a ‘not secure’ sign, it is plausible that they will think before browsing through the site.
With the launch of Chrome 68, numerous sites began switching from HTTP to HTTPS, without any idea as to what that is and how to execute it appropriately.
So we shall begin with understanding the basics of the term HTTP and HTTPS and move on to cover almost every aspect of switching from HTTP to HTTPS.
What is HTTP?
HTTP is an abbreviation of Hypertext Transfer Protocol, and it transfers data from a web server to a browser, allowing users to access and operate numerous web pages.
What is HTTPS?
The difference between HTTP and HTTPS is just the ‘S’ and a rather powerful word attached to this one letter: Secure, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. The job of HTTPS is no different than HTTP but the nature of the data that it transfers is different.
The data transferred by HTTPS is encrypted; meaning that your data is secure from hacking and unauthorized extraction. To change your site from HTTP to HTTPS you need an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate.
Why should you switch from HTTP to HTTPS?
When you switch or migrate from HTTP to HTTPS, you’ll see numerous changes in different areas of your site.
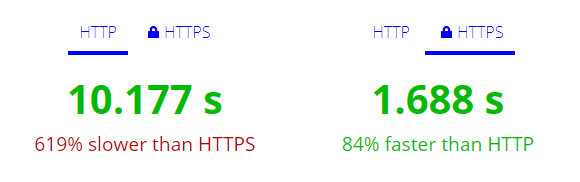
1. Website loading time
When you migrate to HTTPS, your site starts loading faster.
2. Search engine optimization (SEO)
If your domain hosting is HTTPS rather than HTTP, the effect will clearly be visible in your site’s SERP rankings: sites with HTTPS will rank higher than sites with HTTP.
Moreover, security is a top priority for Google and for several other search sites, and so HTTPS has been regarded as a ranking signal.
3. Monitoring traffic
Google Analytics (GA) is a great tool for giving you information related to your site’s growth and audience. Yet, if your site is still HTTP and you’re driving traffic from Quora and Medium, both of which run on HTTPS, then that ‘referral’ traffic will be tracked under direct traffic, making it impossible to monitor referral traffic driven from those platforms separately.
4. Trustworthy and credible
Nearly 77% of users are concerned about their data being misused online, and about 28.9% look for the green address bar.
When your site has HTTPS, people are more likely to trust it and consider it as a credible source of information.
5. Data security
As mentioned already, using HTTPS is secure. The user data which is transferred from the browser to the server is encrypted, securing it from extraction and being used without authorization.
What are the HTTPS certificate types?
There are numerous HTTPS certificates that you can opt for:
1. Domain validation
When you purchase Domain Validation (DV), users will see the lock sign, signifying a secure connection to the server.
![]()
Clicking on the menu button will show:
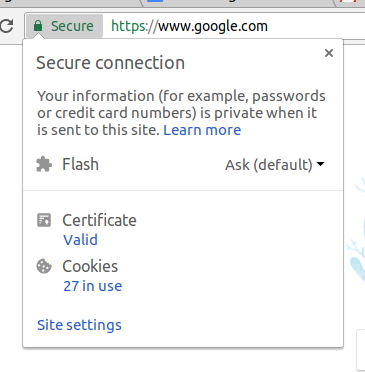
For more information, click on ‘learn more’ and you’ll be redirected to a page that describes the HTTPS and domain security in detail.
This is one of the most common and most affordable types of HTTPS certificates available.
2. Extended validation
This form of certificate is extended beyond domain validation; you’ll still get the secure sign, but your users will also see the domain is legally verified by a CA (Chartered Accountant) and so the legal company name is also displayed.
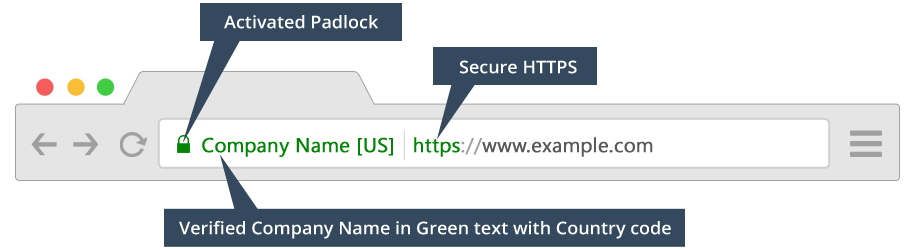
This is considered the most trustworthy form of validation.
3. Organization validation
Similar to the Extended Validation, this certificate doesn’t display the organization name and so is not a popular choice.
How to switch from HTTP to HTTPS
Finally.
How do you switch from HTTP to HTTPS? Before you get started, it’s important to liaise closely with your IT team as you will need their input in order to implement the necessary changes.
Let’s begin.
1. Purchase the right certificate and set it up on your server
Amongst the aforementioned certificates, purchase the one that seems appropriate for your business. Talk with your IT Team to determine which one is right for you and once you’ve purchased the certificate, it will be down to IT to install it on the server.
2. Check every subdomain
After you’ve purchased the certificate and installed it on your server, you should begin checking all the subdomains of your site, including the images.
If even a single image still has HTTP, your domain is vulnerable to hacking.
3. Analyze how many external links are leading to the old HTTP domain
If you have a link building strategy, you will now need to check how many of the links are leading to an HTTP domain. You can do this with free tools, like this one from RankWatch.
Redirect those pages to your HTTPS domain. If you delay in doing this, Google will automatically redirect visitors to an error page.
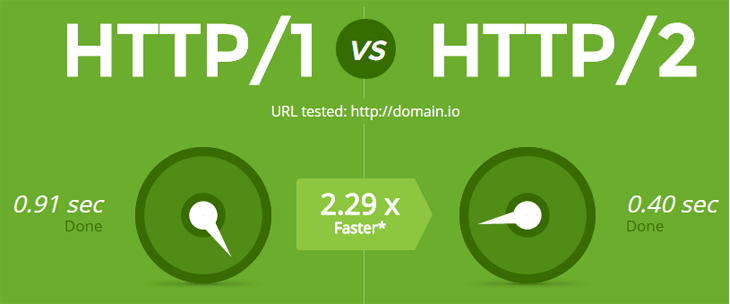
4. HTTP/2
Whilst HTTPS makes your site load faster, you can increase this load time even more with HTTP/2.
5. Don’t forget about SEO
When you’re updating anything on your site, it’s necessary to update your SEO as well.
You can begin by updating sitemaps and correcting canonical tags, etc. Doing so will allow Google to effectively crawl every page of your site and rank it without flagging your site as ‘not secure’.
6. Update HTTPS on google
If you use Google Search Console and Google Analytics, you will need to update the domain from HTTP to HTTPS.
Once you’ve done that, you can then start updating the information on each platform you have an account with.
Access the latest business knowledge in Marketing
Get Access




Comments
Join the conversation...